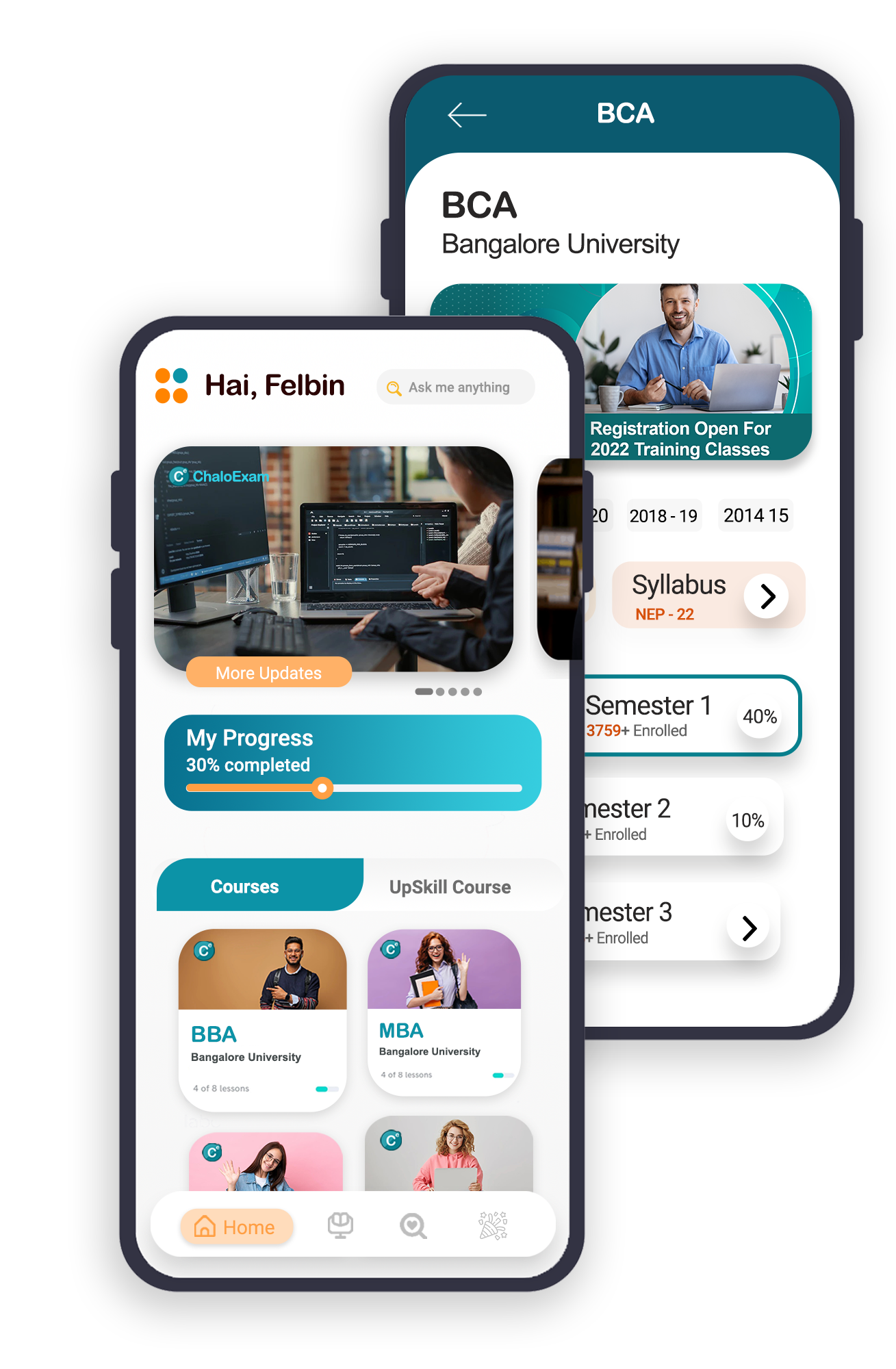
Book Free Classes
Bangalore University 4th Sem BCA Study Materials
Download free BCA 4th sem module wise notes, latest solved question papers, previous 5 years question paper till 2021, model question papers, easy notes, exam oriented notes are available on this website chaloexam.com of Bangalore University
Visual Programing
Visual Programing
Visual Programing
Unix Shell programming

Unix Shell programming
Unix Shell programming
Operation Research
Operation Research
Operation Research
Bangalore University BCA syllabus
Syllabus
Syllabus
FOURTH SEMESTER BCA
BCA401T: INDIAN LANGUAGE
Syllabus as per the one prescribed for science courses of Bangalore University.
BCA402T: ENGLISH
Syllabus as per the one prescribed for science courses of Bangalore University.
BCA403T: VISUAL PROGRAMMING
Total Teaching Hours : 60 No of Hours / Week : 04 Unit - I
Introduction to Visual Programming: The intergrated Development Environment – menu bar, tool bar, from designer, project explorer , properties window , from layout window , The Visual Programing editor. The form object: Properties , events and methods pf forms ; Properties – Name , Captain , Backcolor, Borderstyle , controlbox , maxbutton , minbutton, moveable, startup position , height, width , left, top, scalemode, window, state ; Events –load ,unload , Clerk, Activate , Deactivate , Resize, methods – Show , hide , cls , Unload ,print , Controls –Properties and events of different controls such as command buttons , labels , textboxes image controls , timer, horizontal and vertical scroll bars , option buttons , check boxes , frames lists and combo boxes. Predefined Dialog Boxes – MsgBox and InputBO
[ 12 Hours ] Unit - II
Programming: Data types, variables; declaration and scope arithmetic operations, Study of form and code modules, private and public procedures , Main o procedure , Suba and Functions. Mathematical and string Functions; Branching and Looping Statement ; If – Then , if –Then –Else and Nested If Statements; Select Case –different forms; For – Next , While – Wend and Do – Loops statements ; Arrays- declaration . Static and dynamic arrays. Array and Function, menus and toolbars-Creating menus and toolbars, Working with the menu editor , Designing Multiple Document interface forms. Microsoft common controls.
[ 12 Hours ]
Page 23 of 38
Unit - III
OOP methods and properties of an object, class Modules , Encapsultation and Inheritance characteristics Dynamic Link Libraries (DLLs) and Windows API ; Designing Help files ; File handling – Sequential ,Random access and Binary files, Database connectivity – DAO and ADO Tables and Queries, ActiveX Data objects.
[ 12 Hours ] Unit – IV
Visual C++ Programming: Objects-Classes-VC++Components – Resources-Event Handling – Menus – Dialog Boxes – Importing VBX Controls – Files – MFC File Handling – Document View Architecture – Serialization.
[ 12 Hours ] Unit – V
Interfacing Other Applications – Multiple Document Interface (MDI) – Splitter Windows – Exception Handling – Debugging – Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) – Database Application – DLL- ODBC.
[ 12 Hours ] Text Books:
Gurumit Singh, “Visual Basic 6”, First Edition, Firewall Media, 2007. Reference Books:
1.Charles Petzold, “Windows Programming”, 5th Edition, Microsoft Press, 1999. 2.Steve Holzner, “Visual C++ Programming”, Second Edition, PHI, 1994. 3.Go ttfried, “Programming with Visual Basic 6”, PHI, 2000.
BCA404T : UNIX PROGRAMMING
Total Teaching Hours : 60 No of Hours / Week : 04 Unit - I
Introduction: History, salient features, Unix system architecture, Unix command format, Unix internal and external commands, Directory commands, File related commands, Disk related commands, general utilities. Unix File System: Boot inode, super and data block, in-core structure, Directories, conversion of pathname to inode, inode to a new file, Disk block allocation. Process Management: Process state and data structures of a Process, User vs, kernel node, context of a Process, background processes, Process scheduling commands, Process terminating and examining commands.
[ 12 Hours ]
Unit - II
Secondary Storage Management: Formatting, making file system, checking disk space, mountable file system, disk partitioning, file compression. Special Tools and Utilities: Filters, Stream editor SED and AWK, Unix system calls and library functions, Processes, signals and Interrupts, storage and compression facilities.
[ 12 Hours ] Unix - III
Shell Programming: Vi editor, shell types, shell command line processing, shell script features, executing a shell script, system and user-defined variables, expr command, shell screen interface, read and echo statement, command substitution, escape sequence characters, shell script arguments, positional parameters, test command, file test, string test, numeric test. [ 12 Hours ]
Unit – IV
Conditional Control Structures-if statement, case statement Looping Control Structure while, until, for, statements. Jumping Control Structures – break, continue, exit. Shell Programs covering the above concepts. [ 12 Hours ]
Page 24 of 38
Unit – V
Unix System Communication: Introduction, write, read, wall commands, sending and handling mails. System Administration: Roles of a System Administrator, File System Maintenance, System Startup and Shutdown, User Management, Backup and Restore, Doemons, Domain Name System DNS, Distributed File System.
[ 12 Hours ]
Text Books:
M.G.Venkateshmurthy, “Introduction to UNIX & SHELL Programming”, First Edition, Pearson Education, 2004.
Reference Books:
Forouzan,“Unix and Shell Programming”, 1st Edition,2008 Cengage Learning India
UNIX and Shell Programming, Archana Verma, Firewall Media.
BCA405T: OPERATIONS RESEARCH
Total Teaching Hours : 65 No of Hours / Week : 05 Unit - I
Linear Programming Problems: Origin and development of operations research, Linear Programming Problem –formulation of Lenear Programming problem, Graphical solution. Theory of simplex method. Use of artifical variables and their solution. [ 13 Hours ]
Unit - II
Transportation Problem: Mathematical formulation of transportation problem, Initial basic Feasible solution, North West corner rule, Matrix minima method, Vogel’s approximation method, MODI method to find optimal solution.
[13 Hours ]
Unit - III
Assignment Problem: Mathematical formulation of an Assignment problem, Assignment algorithm, Hungarian Method to solve Assignment Problem.
[ 13 Hours ]
Unit - IV
Network Analysis: Basic components of Network, Rules for drawing Network diagram Time calculation in Networks. Critical Path Method and PROJECT Evaluation and Review Techniques. Algorithm and flow chart for CPM and PERT.
[ 13 Hours ]
Unit - V ` Theory of Games: Two –person Zero –sum Games, the maximin and Minimax principle, Saddle point and value of the Game. Game without saddle points, mixed strategies, solution for 2X2 games, Graphical method Dominance property.
[ 13 Hours ] Text books:
Taha, “Operations Research”, 7th edition, Pearson Education, 2007. References Book:
Billey E. Gillett, “Introduction to Operations Research” , Himalaya Publishing House, Delhi, 1979.
Hamady A.Taha “Operations Research” , Collin Mac Millan, 1982.